Workplace safety has become one of the major priorities for organizations worldwide. While many organizations have a good plan for a structured and well-designed workplace, it is important to define and understand the potential sources of hazards. The National Institute of Health estimated that around 3 million people are exposed to bloodborne pathogens every year.
However, the impact is not limited to the healthcare domain. Employees in commercial and industrial facilities are also at higher risk because they often come into contact with heavy machinery, sharp objects, or other potentially infectious materials. Read on to learn more!
Blood Pathogens- What are they?
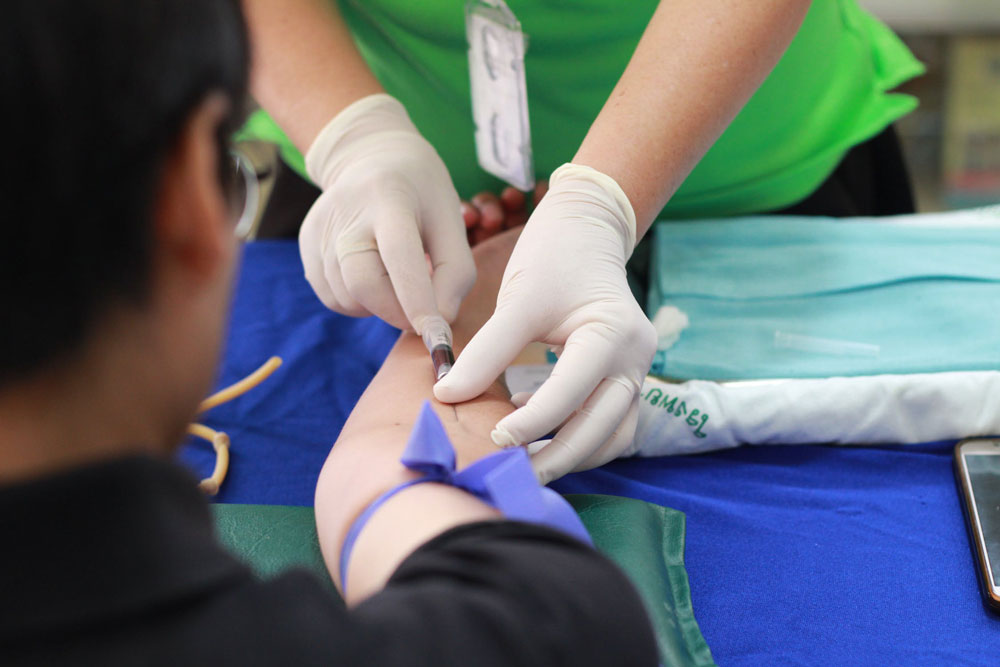
Bloodborne pathogens are infectious diseases that can spread through blood and other bodily fluids. These pathogens include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and prions. Some common bloodborne pathogen conditions are:
- HIV: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a well-known bloodborne pathogen that affects the immune system, leading to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). In the workplace, the risk primarily arises from contact with contaminated blood, such as needlestick injuries.
- HBV: HBV (Hepatitis B virus) is a bloodborne pathogen that primarily affects the liver, resulting in chronic liver diseases. Transmission in the workplace can occur through contact with infected blood or saliva. HBV is highly contagious and can survive outside the body for an extended period. Hence, the virus is a significant concern in the workplace.
- HCV: HCV (Hepatitis C Virus) is another viral infection that also targets the liver. Transmission is similar to HBV and occurs primarily through infected blood. Employees may be at risk if they come into contact with contaminated blood or share equipment that has not been properly sterilized.
OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard for Workplace Safety
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) is the federal agency in the US responsible for enforcing safety and health regulations in the workplace. OSHA’s bloodborne pathogens standards set forth requirements for reducing the risk of exposure to infectious pathogens. The regulations apply to various industries, from healthcare to construction. Here’s an overview of how OSHA regulations apply to the workplace:
- Exposure Control Plan – Organizations must develop and implement an exposure control plan that explains the procedures for minimizing bloodborne pathogens. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE), safe work practices, proper cleaning and disinfection protocols, and a system for handling and disposing of sharp objects.
- Hazard communication standard – OSHA regulations mandate that every organization maintain a safety data sheet (SDS) for the use of chemicals, train employees on their hazards, and ensure that chemicals are properly labeled and stored.
- Recordkeeping – OSHA emphasizes the importance of maintaining records of workplace injuries and illnesses. Companies need to keep records of bloodborne pathogen incidents, accidents, and chemical exposures.
Best Practices to Prevent Bloodborne Pathogen Transmission
Bloodborne pathogens pose significant risks in various professional settings. Preventing the transmission of these pathogens is crucial to protect the workplace. The following are the best practices to prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens in the workplace:
- Safe Handling and Disposal: Employees must be trained to handle needles and equipment carefully. This training helps prevent accidents and reduce the risk of exposure. Proper disposal practices are crucial to ensure the safe containment of used sharps.
- Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Employees should learn to use proper PPE, such as gloves, masks, and eye protection. PPE creates a barrier between employees and infectious materials, thereby reducing the risk of transmission.
- Proper Sterilization and Disinfection Practices: Following OSHA’s sterilization and disinfection protocols is vital to ensure a clean and safe working environment. Employees need to understand the proper methods for cleaning and sterilizing equipment to prevent contamination.
- Training and education: OSHA encourages organizations to train their employees regarding workplace safety against blood-borne pathogens to ensure their safety. Bloodborne pathogen training instills the employees with the knowledge to respect themselves against health hazards from exposure to blood and potentially other infectious material.
- Recognizing Signs of Exposure: Employees should be educated on recognizing symptoms or signs of exposure to bloodborne pathogens, including contact with contaminated fluids or needlestick injuries. Early recognition allows for immediate action, reducing the risk of infection.
Benefits of Bloodborne Pathogen Training
To ensure workplace safety and prevent the spread of infectious diseases, OSHA recommends bloodborne pathogen training for employees. Here are more benefits of enrolling in the training:
- Improved Workplace Safety: By equipping employees with knowledge about bloodborne pathogens, companies can build a safer working environment. Employees will know how to identify potential risks and prevent infections, thereby reducing accidents and safeguarding their health.
- Compliance with Regulations: According to OSHA, every organization should undergo bloodborne pathogens training to protect the well-being of its employees. Meeting these requirements ensures legal compliance and shows the organization’s commitment to prioritizing worker welfare.
- Reduced Liability: Proper bloodborne pathogens training gives employees the confidence and essential skills to handle hazardous situations. This training reduces the risk of accidental exposure and liability issues for the company.
- Better Employee Engagement: When organizations invest in employee safety through bloodborne pathogens training programs, they foster a culture of care and trust. This investment makes employees feel valued, leading to better job satisfaction, improved morale, and increased productivity.
Ensure the Well-Being of your Workforce
Bloodborne pathogens are hazardous microbes that can be transmitted through bodily fluids. Understanding bloodborne pathogens, learning how to adopt preventive measures, and raising awareness can ensure workplace safety. Employees can secure their well-being in the workplace by adequately washing their hands and using personal protective gear. By enrolling in bloodborne pathogens training, employees can protect themselves and others against transmission, creating a safer and healthier workspace for all.
Keep an eye for more news & updates on Times Radar!